Science with impact
Unlocking Impactful Science: Where Research Meets Impact
At the heart of every breakthrough, science leaves an indelible mark on society, shaping our world, driving progress, and fostering innovation. Through our commitment to ‘science with impact,’ we strive to not only pioneer new discoveries but to make a tangible difference in the lives of people everywhere. Grounded in our mission, our pursuit of impactful science sets the stage for transformative change, empowering us to address the most pressing challenges of our time and pave the way for a brighter future.
Our flagship contributions
Between the 2018-2023 period, several scientific contributions were delivered by INESC TEC team. We have selected five of our major contributions as an R&D unit.
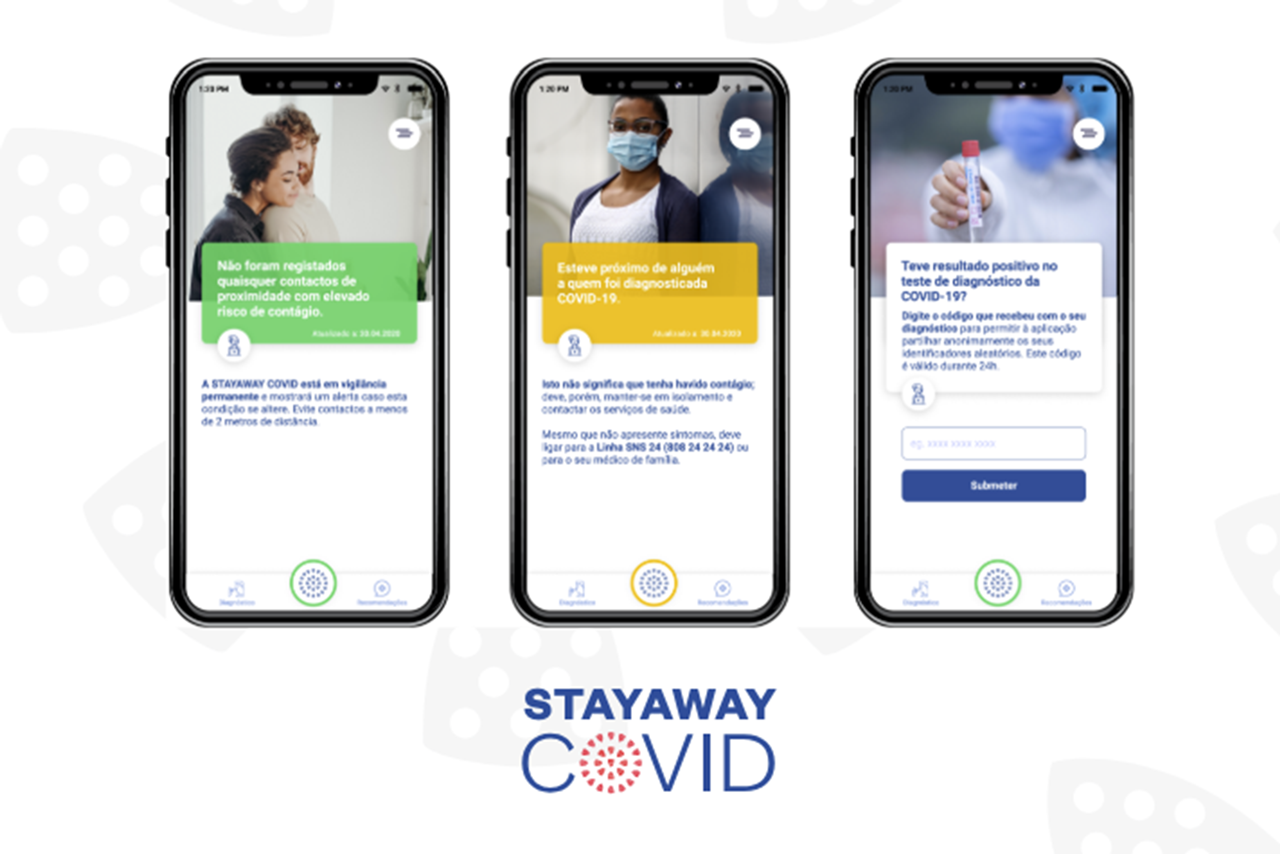
STAYAWAY COVID


1. App STAYAWAY COVID.
2. Explanatory video about the app, produced by INESC TEC.
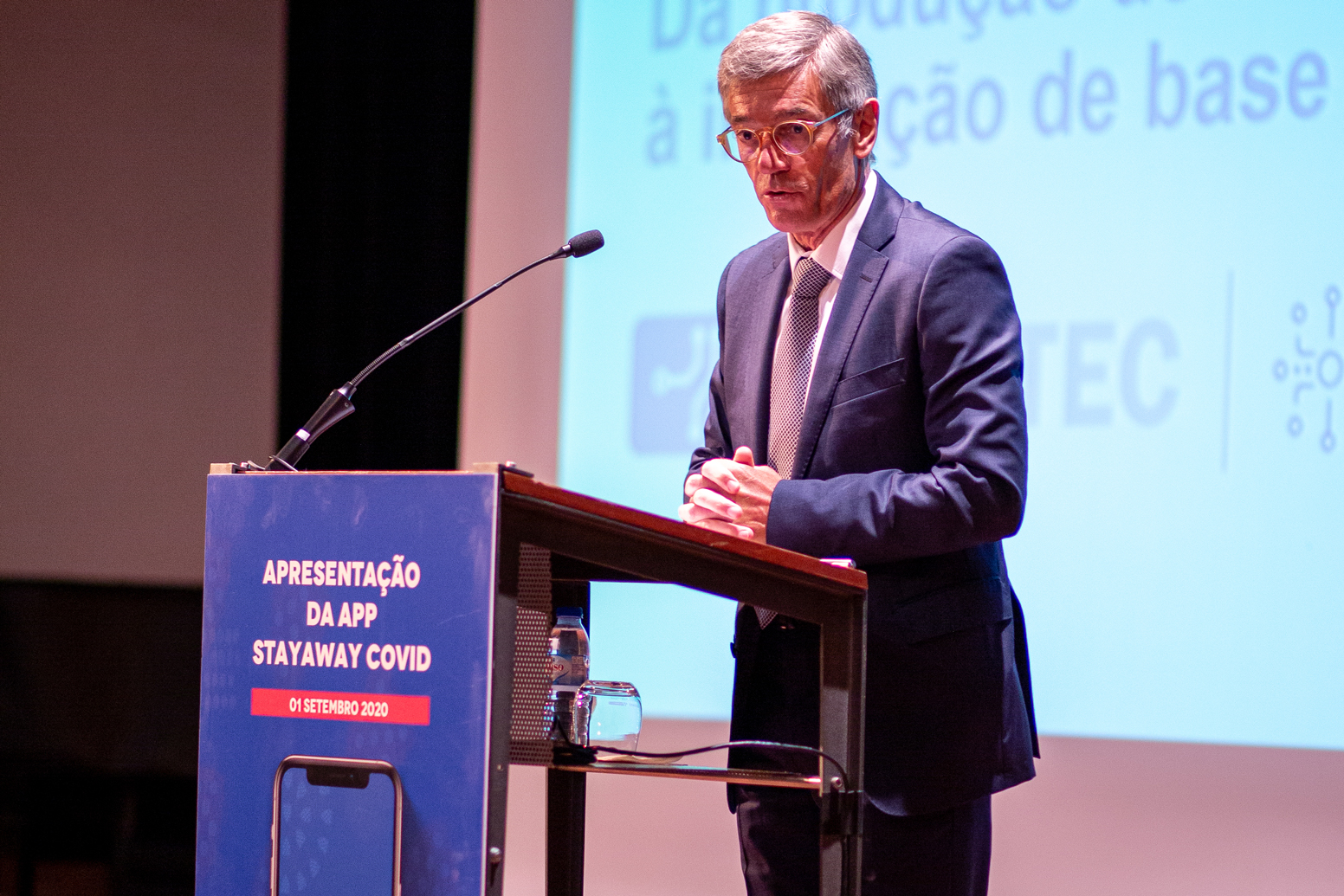
3. José Manuel Mendonça, former INESC TEC president, presented the app in its first public session, with the presence of the Portuguese Government, in 2020.
Decentralised Privacy-Preserving Proximity Tracing
During the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic, research teams at INESC TEC quickly mobilized to explore how their expertise could be harnessed for the greater good. Focused on merging their knowledge in security and privacy with innovative approaches to collaborative exposure notification, the teams embarked on a mission to contribute meaningfully to the global fight against the virus.
Their efforts culminated in a partnership with nine respected research teams from across Europe, under the DP3T project led by Carmela Troncoso at EPFL. This collaboration resulted in the co-authorship of a groundbreaking paper, recognized for its exceptional ability to balance privacy concerns with effectiveness. The proposed algorithm, highlighted in the seminal DP3T paper, garnered praise for its innovative approach to decentralized privacy-preserving proximity tracing.
However, the road to success was fraught with challenges. Initially, the teams grappled with competing proposals that compromised user privacy. Subsequently, they tackled the practical implementation of DP3T, a feat that was made possible through the adoption of core principles by tech giants Google and Apple.
One notable achievement was the design and launch of Stayaway COVID, Portugal’s government-endorsed exposure notification system. INESC TEC played a pivotal role in this endeavor, managing the technical architecture and integration with national health service IT systems. Their dedication ensured the system’s widespread adoption, with over three million downloads and an impressive five-nines availability rate.
The impact of exposure notification systems, including Stayaway COVID, was underscored in a study published in Nature, which credited these technologies with influencing the trajectory of the pandemic and ultimately saving lives. As the landscape of the pandemic evolves with the advent of vaccines and increased knowledge of the virus, exposure notification systems continue to stand as a testament to the power of collaborative scientific innovation in times of crisis.Clipping
Newsroom
ClippingClippingClippingClippingNews pieceTransmission-Distribution Systems Coordination



1. INESC TEC researcher working at INESC TEC Laboratory of Smart Grids and Electric Vehicles.
2. App developed under the scope of the InterConnect project, led by INESC TEC.
3. INESC TEC researcher working on a prototype of the InteGrid project.Contribute towards improved management and information exchange between transmission system operators (TSO) and distribution system operators (DSO) while enabling the integration of distributed energy resources (DER) flexibility.
A pioneering concept of flexibility areas was first introduced and later refined to address the intricate interconnections between transmission system operators (TSOs) and distribution system operators (DSOs) using data-driven network equivalents. This concept ignited inspiration among research groups such as LIST and the University of Melbourne, leading to further advancements in the field. Additionally, the proposal of grey-box dynamic models has significantly contributed to enhancing the analysis of transmission system frequency and voltage stability while safeguarding sensitive network information.
These advancements were put into practice in EU projects like TDX-ASSIST and EU-SysFlex, where coordinated operational planning between TSOs and DSOs was successfully demonstrated in real-world meshed grids through the computation of flexibility maps. Stochastic algorithms were also developed to assist DSOs in adhering to agreed-upon reactive power levels at TSO-DSO interconnections, effectively utilizing local flexibility from distributed energy resources (DERs) while mitigating the impact of renewable energy forecast uncertainty.
Furthermore, contributions were made towards the effective and standardized procurement of flexibility via DSO-oriented services, ensuring the confidentiality of sensitive network data. A grid segmentation strategy was proposed to aggregate DERs capable of addressing grid constraints without causing additional limitations, thus enhancing coordination efforts. These algorithms were validated in real distribution networks through projects such as EUniversal, integrating seamlessly with DSOs like E-REDES and market clearing platforms such as N-SIDE.Clipping
Newsroom
Press ReleaseNews pieceNews pieceAlgorithms for UAV-assisted wireless networks



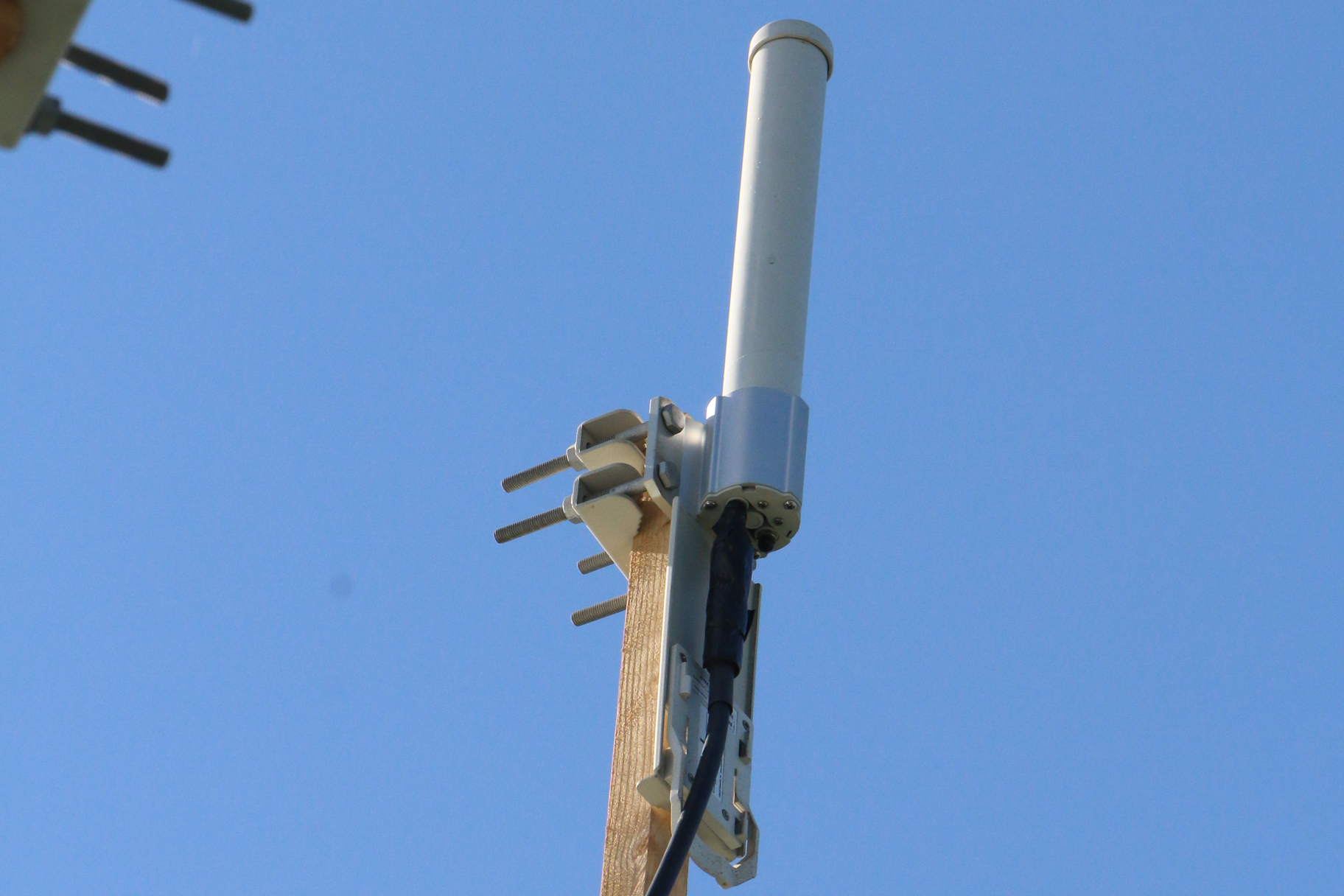
1. Wireless technology of the WISAT project being tested at INESC TEC headquarters.
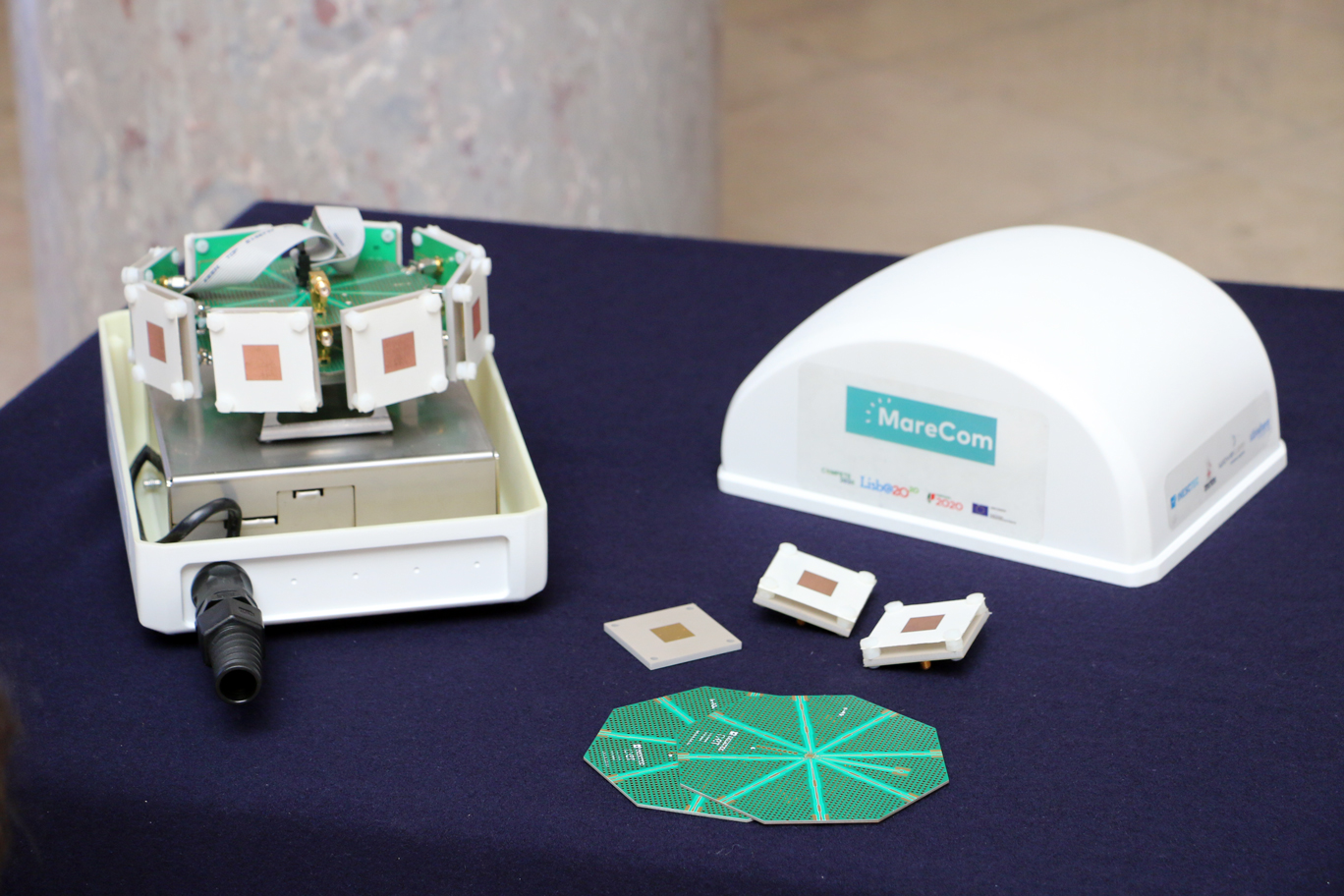
2. MareCom project prototype, developed by INESC TEC.
3. Wireless technology developed under the scope of MareCom project.
Pioneering algorithms for UAV-assisted wireless networks.
The focus of this contribution centered on the development and implementation of pioneer algorithms for aerial networks, marking a significant leap forward in enhancing network performance, efficiency, and adaptability. This endeavor encompassed innovative solutions in position control, routing, and active queue management, specifically tailored to meet the unique challenges of aerial communication networks.
These algorithms were accurately crafted to tackle critical issues in network management, ranging from optimizing throughput and minimizing delay to ensuring efficient resource allocation and enhancing overall network reliability and responsiveness. The results achieved through these efforts not only surpassed existing state-of-the-art methodologies in terms of performance gains but also conducted in a new era in the design and operation of aerial networks.
At the core of these advancements lie the position control and routing algorithms, which have demonstrated superiority over traditional approaches by delivering higher throughput and lower delay. By optimizing the dynamic positioning and movement of aerial platforms, these algorithms maintain optimal network connectivity and performance, even in extreme environments. Similarly, the placement and active queue management algorithms further elevate network efficiency by intelligently managing traffic flows and resources, maximizing performance gains without compromising reliability.
The development of traffic-aware and traffic- and energy-aware placement algorithms represents a notable innovation in aerial network management. These algorithms take into account current network load, traffic patterns, and energy efficiency, crucial factors for the sustainability of aerial networks. By enabling significant performance gains while ensuring optimal resource utilization and minimal environmental impact, they set a new standard for the future of aerial network management.Clipping
Newsroom
ClippingClippingClippingNews pieceNews pieceInventory and Pricing Models



1. Project between INESC TEC and IKEA being presented at INESC TEC Industry and Innovation Lab.
2. INESC TEC Industry and Innovation Lab facilities.
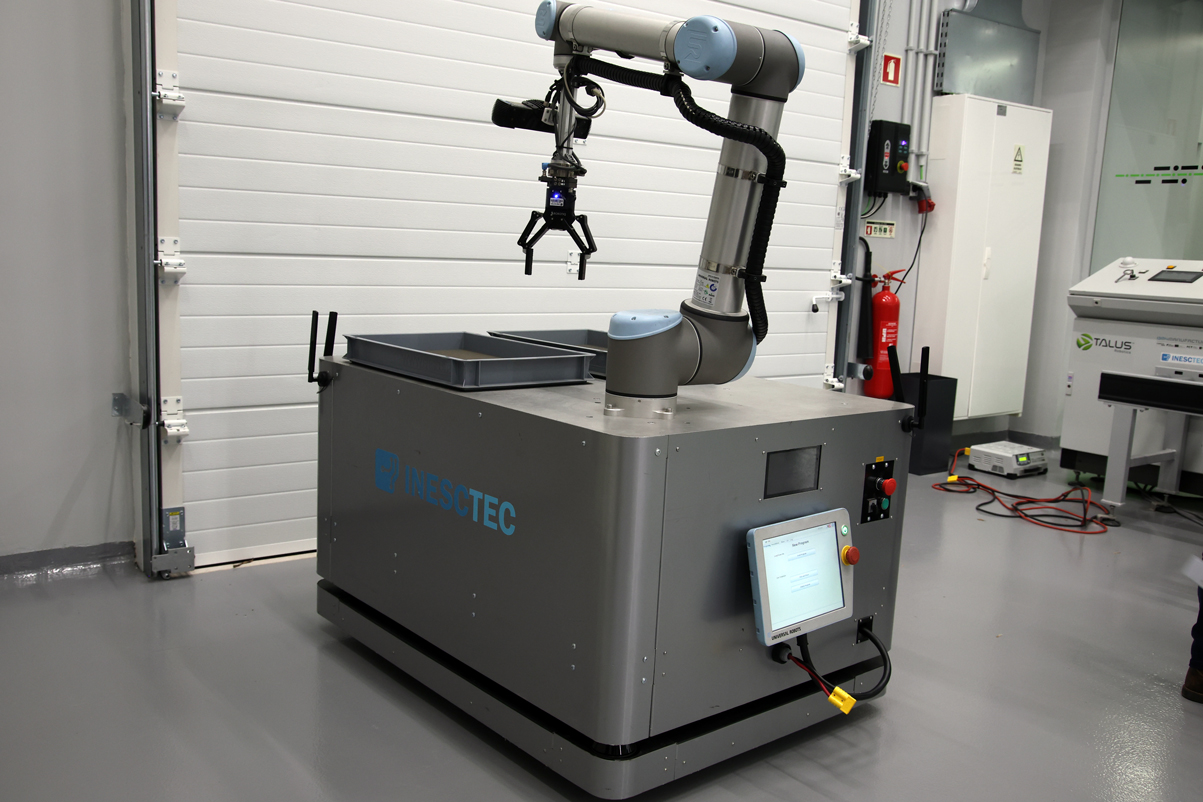
3. INESC TEC robot operating at the institution Industry and Innovation Lab.
Strategic Inventory and Pricing Models for Omnichannel Retail Optimisation.
Omnichannel retailing, which seamlessly integrates online and offline sales channels, has emerged as a cornerstone of research in retail operations. Since 2015, our contributions have been instrumental in driving advancements in this field, leveraging cutting-edge empirical and analytical models to gain insights into supplier/customer behavior and incorporate it into inventory and pricing decision-making processes for omnichannel retailers, all while navigating the complexities of retail planning in the digital age.
Through collaborations with industry leaders like Sonae (in grocery) and Farfetch (in fashion), our studies have introduced innovative and sometimes counterintuitive policies, resulting in the development of new theories with practical implications. For example, one study revolutionized retailers’ approach to stock reservation for customer service, while another led to a reimagining of incentives between marketplaces and suppliers.
Recognized for their combination of analytical rigor and practical insights, our studies have been published in prestigious journals such as Management Science, Manufacturing & Service Operations Management, and MIT Sloan Management Review, and are frequently cited by both academic and practitioner communities.
Retailers adopting our strategies have reported tangible benefits, including improved decision-making capabilities, enhanced fill rates, accelerated product time-to-market, and increased profitability. Our influence extends beyond academia, as evidenced by seminars conducted at MIT Sloan Management Review.
Building on the success of our initial studies, we have extended our research to the management of perishable products through the Be Fresh project (2022-2024). Aligned with hunger and sustainable consumption Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), this project aims to reduce food waste by optimizing discount and production planning across the food value chain, based on customer response to shelf-life evolution. Preliminary results utilizing a discrete choice model embedded in a proximal policy optimization algorithm indicate the potential to reduce waste by over 20% compared to state-of-the-art policies.News piece
Newsroom
PodcastScience Communication long feature
Quantum Analogue Simulation and Optical computing



1. Technology developed under the scope of the METBOTS project.
2. INESC TEC Imaging Laboratory facilities, at the Faculty of Science of University of Porto (FCUP).
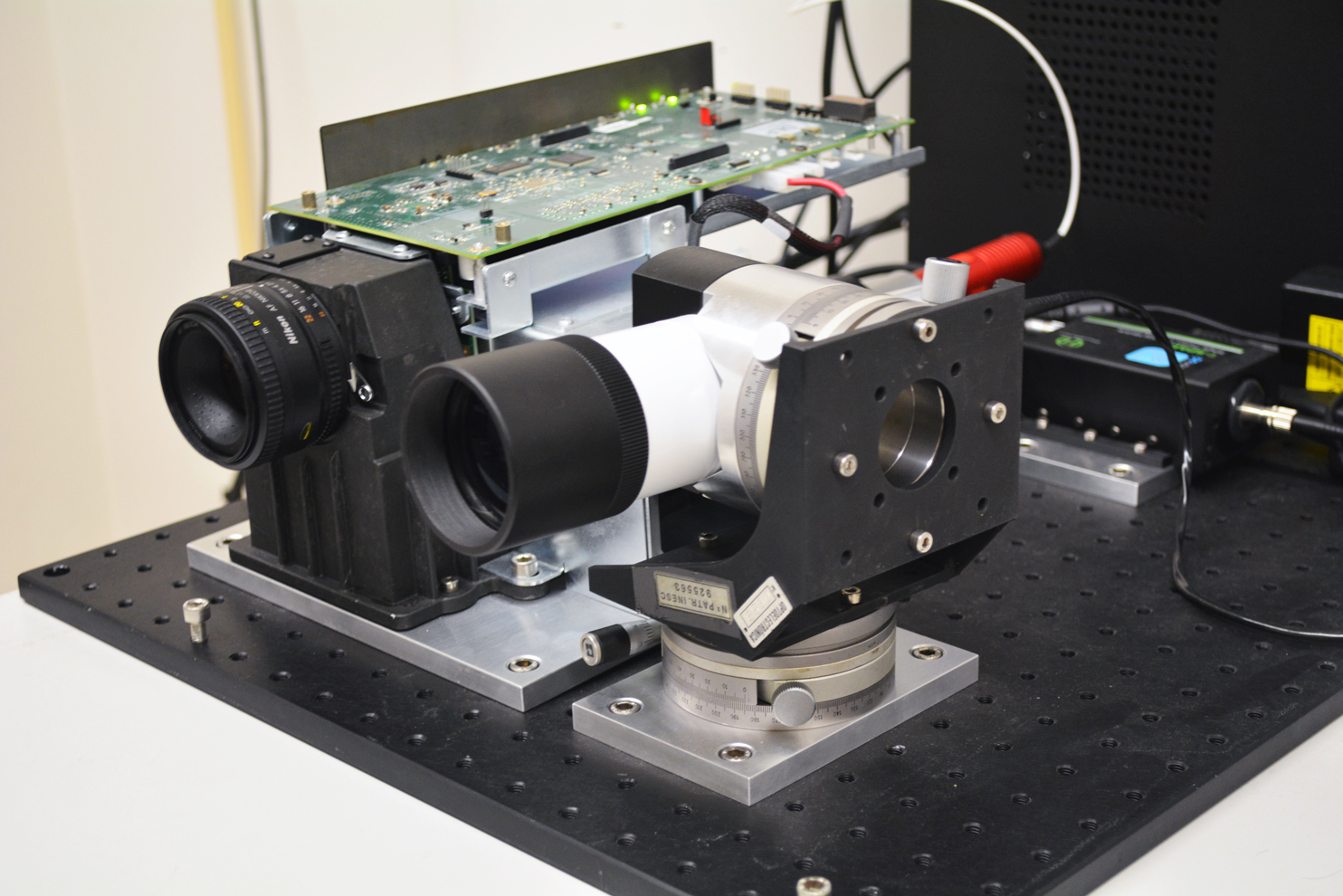
3. INESC TEC prototype being tested at INESC TEC Imaging Laboratory.
Novel experimental platforms for Quantum Analogue Simulation and Optical computing.
The interplay of light propagation in nonlinear media and wavefront shaping techniques presents a captivating realm for the deployment of analogue quantum simulators. This arena showcases a fascinating convergence of coherent wave-like interferometric effects and nonlinear particle-like dynamics. Throughout the evaluation period, the team at INESC TEC has delved deeply into the intricacies of light propagation within nonlinear photorefractive crystals, leveraging their mathematical isomorphism to construct an experimental model for a two-dimensional quantum-fluid, notably a Bose-Einstein Condensate.
Significant achievements have been made in observing characteristic signatures of 2D quantum-like turbulence regimes, marking a significant milestone in our understanding of complex quantum phenomena. Furthermore, high-profile collaborations have propelled the development of physical analogues for alternative models of gravity, shedding light on new frontiers in gravitational physics.
Harnessing the versatility of these platforms, our research has extended to explore their potential in all-optical computing applications. Through the exploitation of strong nonlinear dynamics, we have demonstrated the capability of light-speed data processing in the optical domain. This breakthrough has led to the development of neuromorphic architectures, including optical reservoir computers and extreme learning machines, facilitating unprecedented advancements in computing speed and efficiency. The reported achievements underscore the transformative potential of our research in pushing the boundaries of optical computing and quantum simulation.Podcast
Newsroom
News PieceNews PieceClipping